Monteggia Fracture in children is an example of a potential medical malpractice lawsuit. The current political enviroment would have you believe there are primarilily frivilous medical malpractice lawsuits, but that is not the cae. Healthcare providers, like doctors, are measured by the "standrad of care." The standard of care is determined by the standard that would be exercised by the reasonably prudent healthcare provider. Such a test (known as the 'Bolam Test') is used to determine whether a doctor is liable for medical malpractice. This would be applied in a potential Monteggia Fracture lawsuit. The standard of care is there to help the defendant. When it is determined they met the standard of care, it is unlike a medical malpractice lawsuit will be filed.
What is Monteggia fracture?
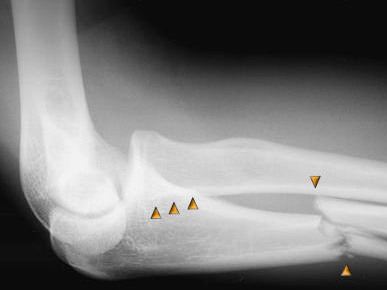
Monteggia fracture is a joint injury that the ulna 1 / 3 fracture and dislocation. Later, many scholars of this injury further observation and mechanism of the injury gradually expanded the scope of the concept, the direction of the radial head dislocation and ulna fracture at different levels or feet radius fracture are included double the damage can be found in all age groups, but mostly children and adolescents. What is etiology of Monteggia fracture? Monteggia fracture is divided into four types, and its pathogenesis are presented below: 1, straight-type Monteggia Fracture: the more common, occur in children. Hyperextension elbow or bit extension falls, forearm supination, touch the palm of your hand, the body mass to gravity along the bottom of the humerus, ulna caused the first 1 / 3 oblique fracture, residual violence, forced dislocation of radial head forward foreign, bone fracture side to the palmar and radial angle. Injury due to direct violence, the fractures were transverse or crushed. 2, flexion type Monteggia Fracture: more common in adults. Micro elbow flexion, forearm pronation-bit touch-palm, the force caused by ulnar higher first plane transverse or short oblique fracture, radial backward foreign dislocation, fracture to the dorsal and radial angle. 3, inside the closed-type Monteggia Fracture: multi-occurred in child care. Elbow extension, forearm pronation, adduction of upper limb a little bit forward fall. Violence since the cubitus to foreign, resulting in ulnar Department Coracoid split cross-sectional or longitudinal fractures, displaced less outward radial head dislocation. 4, a special type Monteggia Fracture: radial head dislocation forward, the merger on the ulna and radius 1 / 3 or the middle and upper 1 / 3 pairs of fractures. This type accounts for about 5% of adults and children may occur. Most scholars believe that: the damage mechanism of fracture with the same extension, but the merger of the radial fracture, radial head dislocation may be, the radial bone trauma caused by the second. What is symptoms of Monteggia fracture? 1, straight-type Monteggia Fracture can be touched in the cubital fossa radial head, shortened forearm, ulna angle forward. 2, available at the elbow flexion Monteggia Fracture after radial head touched, ulna backward angle. 3, inside the closed-type Monteggia Fracture lateral elbow can touch the proximal radial head and ulna angle outward. 4, a special type Monteggia Fracture of radial bone in the elbow before the ulna and radius fracture deformity and there is unusual activity. How is Monteggia fracture diagnosis? Monteggia fracture is diagnosed by X-ray examination: X-ray film in order to avoid missed diagnosis should include the elbow, the attention of the anatomy of the joints brachioradial relationship, if necessary, X-ray film for contralateral control. Where the upper ulna fracture, and the X-ray film did not see when the radial head dislocation, should be to deal with such a fracture, dislocation of radial head because sometimes on their own after the reset. How is Monteggia fracture treatment? Monteggia Fracture requires manual reduction and external fixation. The use of general anesthesia or brachial plexus anesthesia. Reset when the straight-type, 900 of elbow flexion, forearm neutral position against the traction will be the radial and dorsal ulnar bone pushed to make it reset, and then fold the top method used ulna fracture, buckling plaster 900 fixed 8 ~ 10 weeks. Reset flexion, the elbow extension position against traction, the radial head to the ulnar and volar pushed reset, and then reset ulnar fracture, semi-stretch-bit long arm elbow cast immobilization for 6 to 8 weeks. Adduction-type manual reduction after the radial head, ulna and more self-reduction, long arm cast immobilization for 4 ~ 6 weeks. Monteggia Fracture requires open reduction and internal fixation. If manual reduction is not successful; old fracture, radial head can be reset (3 ~ 6 weeks), can be reset operation and, if possible, repair or reconstruction of annular ligament, ulnar deformity correction fixation. Can not be reset if the radial head, the adult radial head resectability, adult children are to be removed later.
Monteggia Fracture Attorney
The medical community recognizes misdiagnosis as a complication of Monteggia Fractures. It also recommends the Bell Tawse procedure to treat Monteggia Fractures. The standard of care is to protect the doctors. When these procedures are not followed due to the doctor's negligence, medical malpractice lawsuit are to protect you. If you believe your doctor's treatment of your Monteggia Fracture was negligent, call 843-722-8070 now for a free consultation.